- 4995 SR-68, Golden Valley, AZ 86413, United States
- Mon - Sat 8.00 - 18.00 Sunday CLOSED
Department
We make it easy to get extraordinary care.
What Is Allergy and Immunology?Allergy and immunology is the area of medicine dedicated to the care and treatment of health concer
What is an anesthesiologist? What training is involved?An anesthesiologist is a doctor (MD or DO) who practices anesthesia. Anesth
OverviewGastric bypass and other weight-loss surgeries — known collectively as bariatric surgery —involve making changes to yo
What is a cardiologist?A cardiologist is a doctor who’s an expert in heart and blood vessel diseases, they can help keep you fro
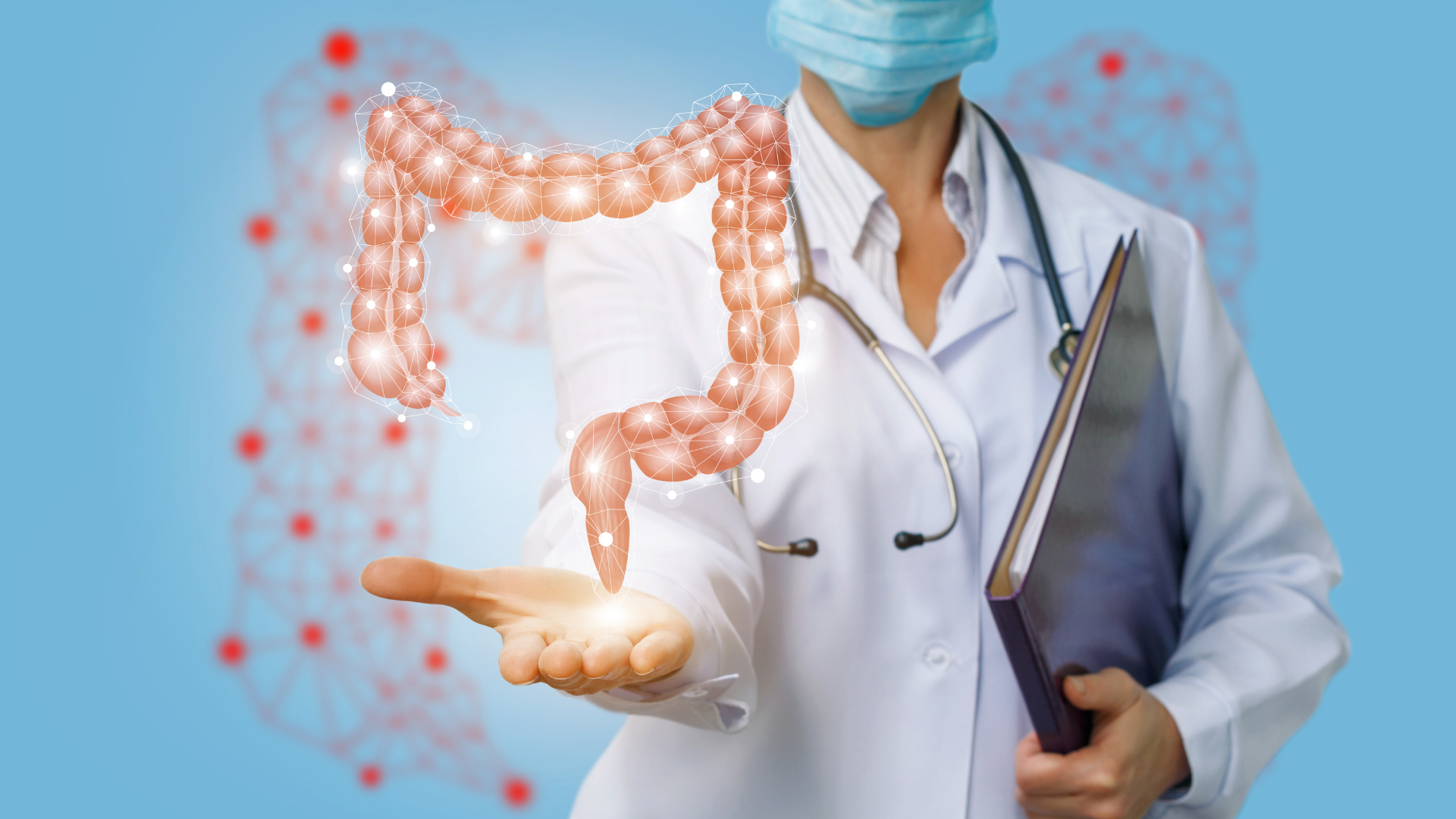
What Is Colorectal Surgery?Colorectal surgeries are procedures that are done to correct a damaged or disease section of your lower
The DisciplineCritical care medicine encompasses the diagnosis and treatment of a wide variety of clinical problems representing t
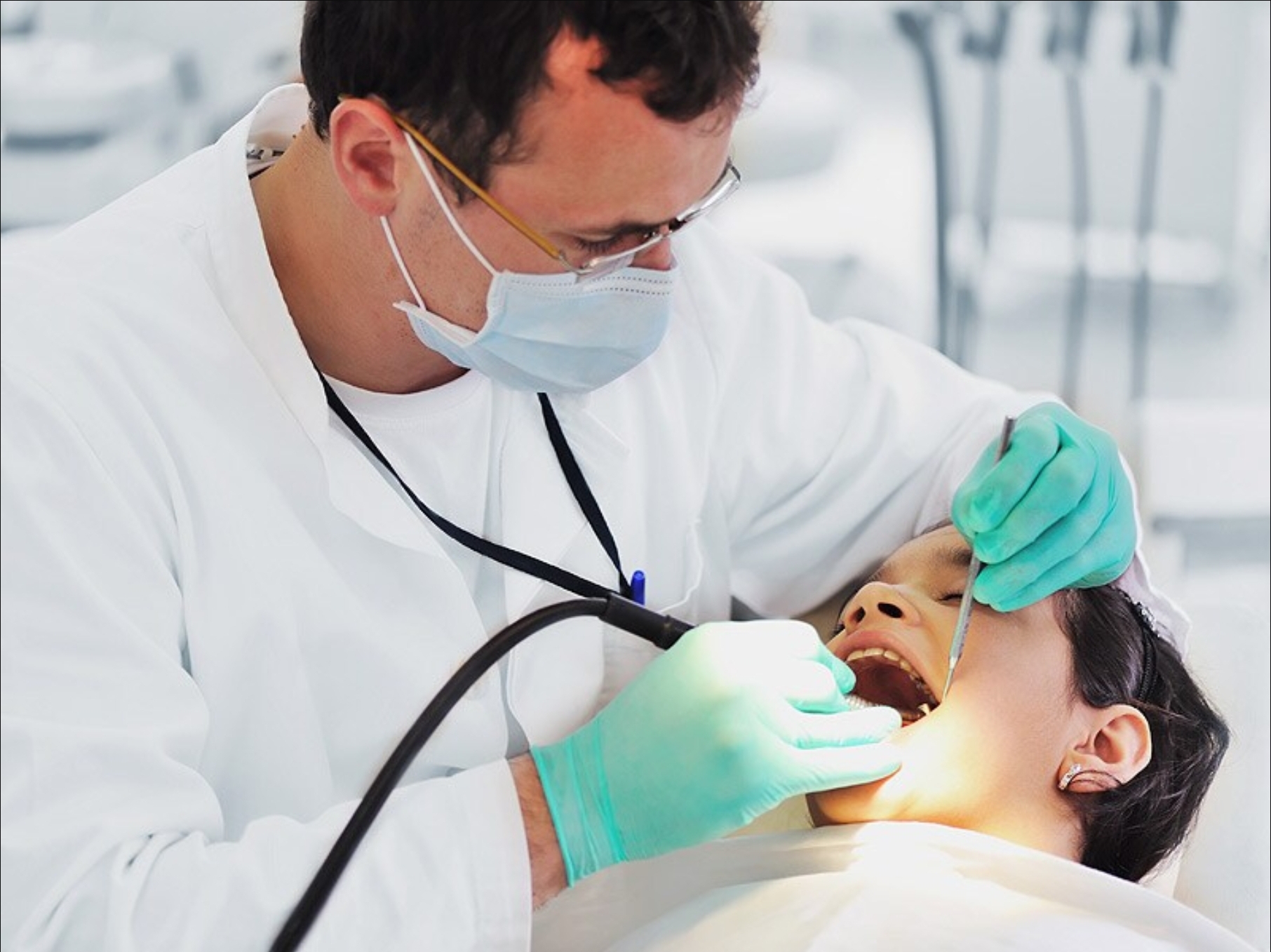
What Does a Dentist Do?A dentist has many responsibilities, and one of the most important is promoting good dental hygiene. T
A dermatologist is a medical doctor who specializes in treating diseases that affect the skin, hair, and nails. You might see a de
Endocrinologists specialize in treating disorders of the endocrine system, the network of hormone-producing glands in your body. E
What is an ENT (Ear Nose and Throat Doctor)?An ear, nose, and throat doctor (ENT) specializes in everything having to do with thos
An eye doctor is a physician who treats eye-related issues. Many people see an eye doctor due to various conditions like pink eye.
Gastroenterology is the study of the normal function and diseases of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon and rectum, pa
Geriatric doctors diagnose and treat issues that affect older adults. Their patients often have one or more chronic health issues.
Infectious diseases are disorders caused by organisms — such as bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. Many organisms live in an
Interventional radiology helps with cancer in a number of ways. It can directly treat the disease, prevent bleeding during surgery
A neurologist is a doctor who diagnoses, treats and manages conditions that affect the nervous system, made up of your brain, spin
Your experience in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology is guided by a team of experts. You'll receive an individualized ca
Occupational medicine, formerly called industrial medicine, the branch of medicine concerned with the maintenance o
Oncology is the field of medicine that deal with the diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and early detection of cancer. Oncolog
An ophthalmologist is a medical or osteopathic doctor who specializes in eye and vision care. Ophthalmologists must comp
An orthopedic surgeon is qualified to diagnose orthopedic problems, perform or prescribe treatments, and assist with rehabilitatio
Pain management is a branch of medicine that applies science to the reduction of pain. It covers a wide spectrum of conditions, in
Veterinarians play a critical role in maintaining the health and well-being of animals, which in turn has a significant impact on